

Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are essential for ensuring manufacturing precision and product quality. Zeiss and Hexagon, two major players in industrial metrology, offer powerful yet distinct approaches to coordinate measurement. This article explores the features, specifications, and use cases of their CMM systems, highlighting their unique strengths without declaring one superior.

Zeiss is synonymous with precision and engineering quality. Their CMM lineup includes bridge-type machines for high-accuracy applications, as well as gantry and optical systems for larger or more complex tasks. Zeiss machines are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
One of Zeiss’s defining features is sensor flexibility. Their systems accommodate tactile, optical, and CT scanning sensors, making them adaptable to diverse inspection needs. Zeiss CMMs are also compliant with ISO 10360 standards, ensuring consistent accuracy and reliability.
The CALYPSO software suite supports comprehensive dimensional analysis and integrates seamlessly with CAD models. It enables automated inspection plans and rich reporting, though it generally requires trained personnel to operate efficiently.
Two flagship models from Zeiss include:
| Model | Measurement Range | Accuracy | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| CONTURA | X: 700–1200 mm, Y: 700–2400 mm, Z: 600–1000 mm | 1.4 + L/350 µm | Bridge-type, multiple probe options, flexible software |
| PRISMO Ultra | Various configurations | 0.5 µm + L/500 | Ultra-high precision, air bearings, damped granite bed |
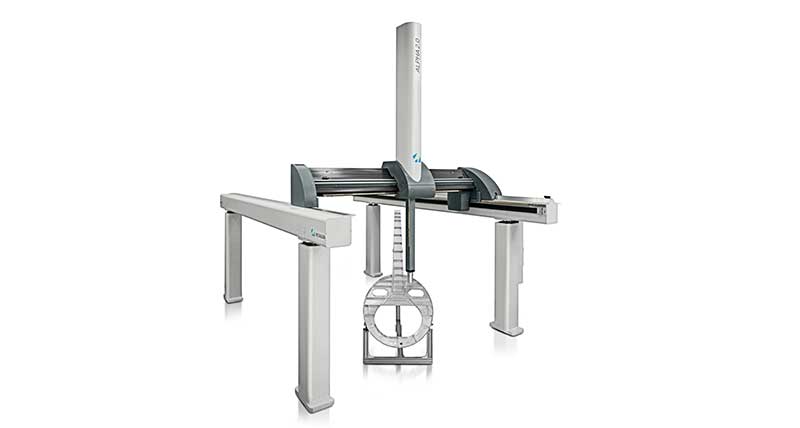

Hexagon is a global leader in metrology solutions, with systems designed for demanding industrial environments. Their CMM portfolio includes bridge, gantry, and horizontal-arm models optimized for versatility and integration.
Hexagon CMMs support a variety of sensors including tactile, laser, and optical, and they offer excellent compatibility with automation systems. The PC-DMIS software is a core strength, allowing users to perform advanced dimensional analysis, integrate CAD data, and automate inspection paths with minimal manual input.
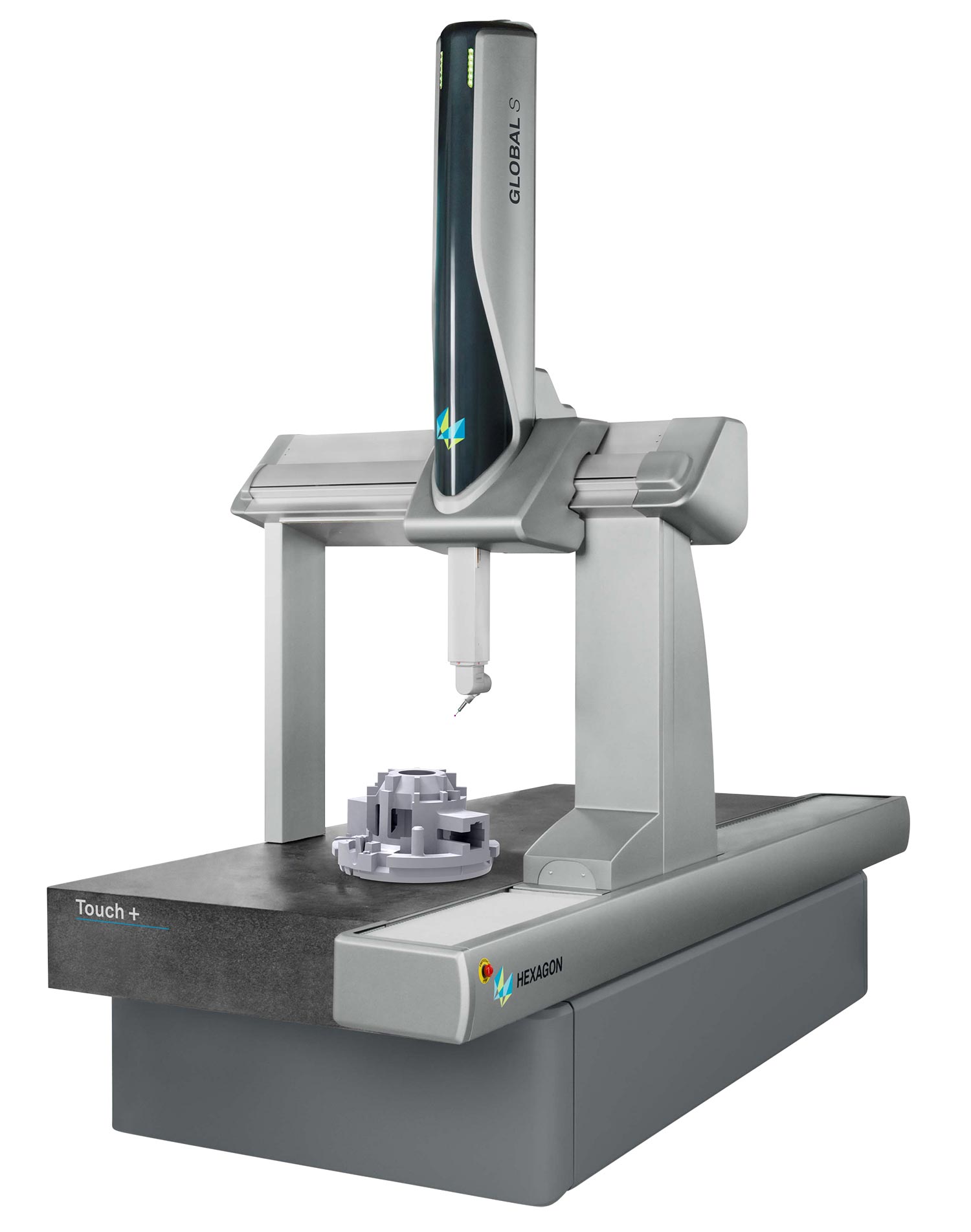
Unlike Zeiss, Hexagon emphasizes sensor integration and user interface improvements, such as touch-screen operation and real-time data visualization. These features allow for greater control and faster adaptation to complex measurement tasks.
Two representative models from Hexagon:
| Model | Measurement Range | Accuracy | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALPHA | Various sizes (e.g., 1200 x 1500 x 1000 mm) | As low as ±1.5 μm | High-accuracy bridge type, flexible for automation, tactile sensor compatible |
| GLOBAL Touch+ | Varies by configuration | ±2 μm typical | Touch-screen interface, optimized for usability, PC-DMIS integration |
Zeiss and Hexagon both offer world-class measurement systems, but their underlying philosophies and application focuses differ in several key areas.
In terms of precision, both manufacturers deliver extremely accurate CMMs. However, Zeiss may hold a slight advantage in ultra-high-precision applications, particularly with models like the PRISMO Ultra that are engineered for exceptional measurement accuracy.
When it comes to sensor flexibility, Zeiss supports tactile, optical, and CT sensors, providing a wide range of inspection options. Hexagon offers a similarly broad sensor lineup but places additional emphasis on multi-sensor automation, enhancing productivity in environments that require frequent probe changes or diverse inspection tasks.
The software environments also reflect different strengths. Zeiss uses CALYPSO, which is deeply integrated with its hardware and designed for structured workflows. Hexagon’s PC-DMIS, on the other hand, is widely adopted across various industries and valued for its versatile programming features and compatibility with a range of platforms.
From a usability perspective, Hexagon systems often feature touch-screen interfaces and customizable automation paths, making them easier to use in production settings. Zeiss systems, while potentially requiring more training, offer high levels of configurability and control, which can benefit users handling complex measurement challenges.
Regarding industry fit, Zeiss systems are frequently chosen for applications in aerospace, optics, and medical devices, where precision and traceability are critical. Hexagon’s solutions are also found in these areas but are particularly strong in automotive and energy sectors, where integration with large-scale production environments is a priority.
Zeiss is well-suited for organizations that demand ultra-high precision, particularly in research, medical, and aerospace sectors. Their equipment supports advanced workflows and complex geometries with unmatched reliability.
Hexagon is ideal for manufacturers looking for flexible, high-speed inspection integrated into automated production lines. Automotive OEMs, energy firms, and general manufacturers will find Hexagon’s systems adaptable and scalable.
Zeiss and Hexagon both offer outstanding CMM solutions that cater to different operational needs. Zeiss focuses on precision, sensor diversity, and deep CAD integration, while Hexagon brings scalable automation and user-friendly interfaces to the forefront. By understanding each system’s strengths, manufacturers can make informed decisions that align with their measurement requirements, workforce skills, and future scalability plans.