

In manufacturing and engineering, two key machines play distinct roles: CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) and CNC (Computer Numerical Control). While both are vital for creating high-quality components, their functions differ significantly. This article will help you understand these differences and choose the right machine for your needs.
CMMs are specialized equipment used to inspect and measure the geometrical characteristics of objects. They utilize a probe to determine precise dimensions along the X, Y, and Z axes, making them ideal for quality control and ensuring parts meet engineering specifications.
CMMs are exceptional in situations where precise measurement is critical. They are typically used in quality assurance processes for various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and tooling. CMMs help detect deviations from design specifications, which ensures the final product’s compliance and reliability.
CNCs are automated systems used to manufacture components by following programmed instructions. Using CAD software, engineers design a component that transforms into machine-readable code. CNCs can handle complex shapes and designs with exceptional precision, making them indispensable for creating parts from metals, plastics, and composites.
CNCs are best suited for applications requiring complex geometries and high production volumes. They are widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics, where consistency and precision are paramount.
In addition, the term "CNC" refers to advanced technology used in various automated machines, such as:
Each machine serves a unique purpose, but they all share one thing in common: they make precise, complex tasks simpler and more efficient.
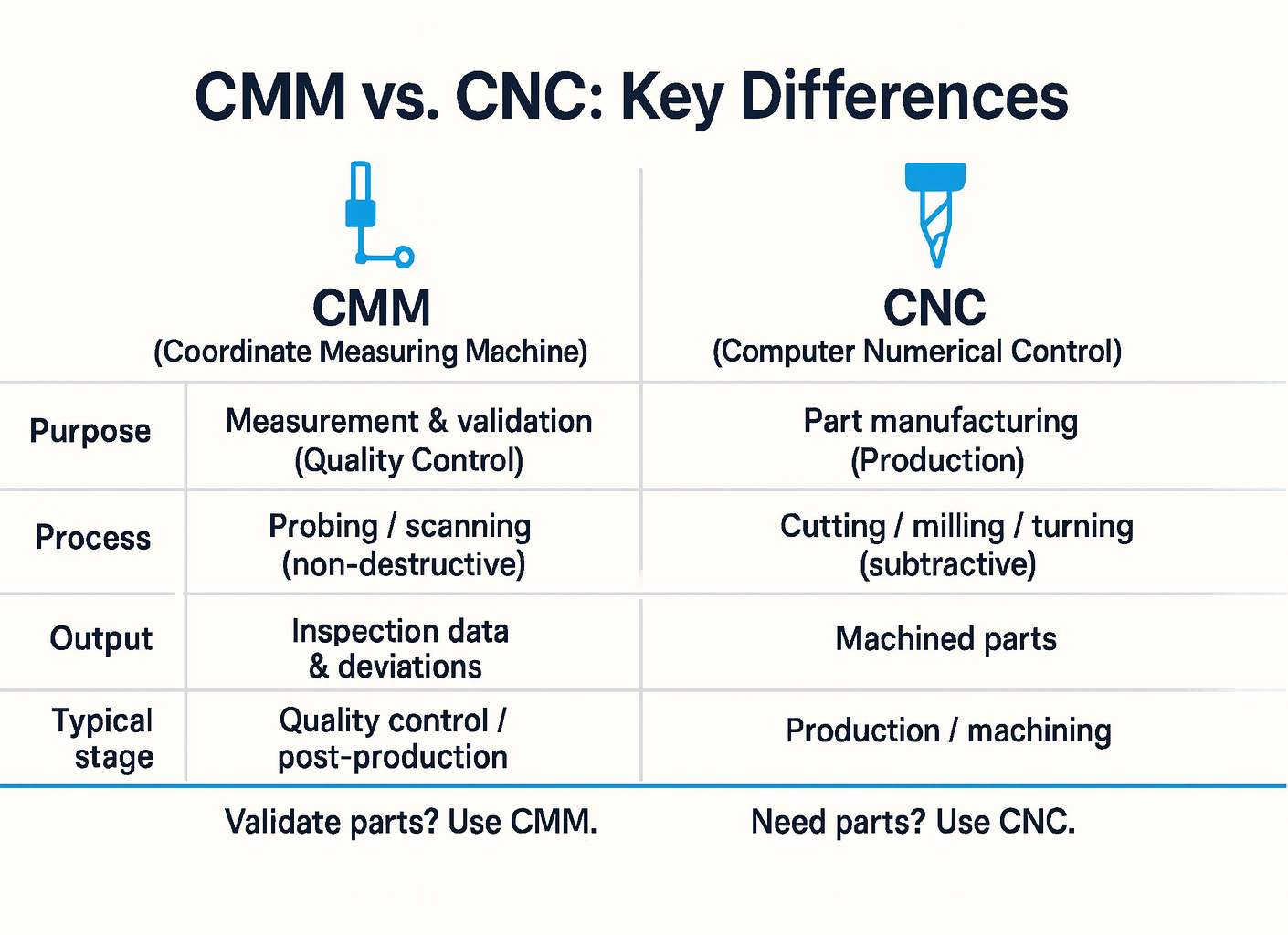
Although CMM and CNC might sound similar, they are fundamentally different machines designed for distinct purposes —CMM for measurement accuracy, and CNC for manufacturing precision.
If you need to make parts, CNC is your choice. For measuring and validating parts, rely on a CMM.
CMMs and CNCs are both vital in manufacturing, but they serve different roles:
In summary, choosing between CMM and CNC depends on your needs—CMMs are for inspection, ensuring that parts meet design standards. CNCs are for production, creating parts with exceptional precision. While they are both essential in modern manufacturing, their roles are entirely different.
Understanding these distinctions will help you streamline your production and quality control processes, ensuring optimal results in both areas.

Source: KEYENCE Website(https://www.keyence.com/products/measure-sys/cmm/xm/index_pr.jsp)
This CMM has a caliper-like feel, enabling even beginners to perform high-precision measurements. It can be carried without the need for temperature control, allowing for immediate measurements at any desired location and time. As it doesn't require a large installation space, it's a CMM with a low entry barrier.
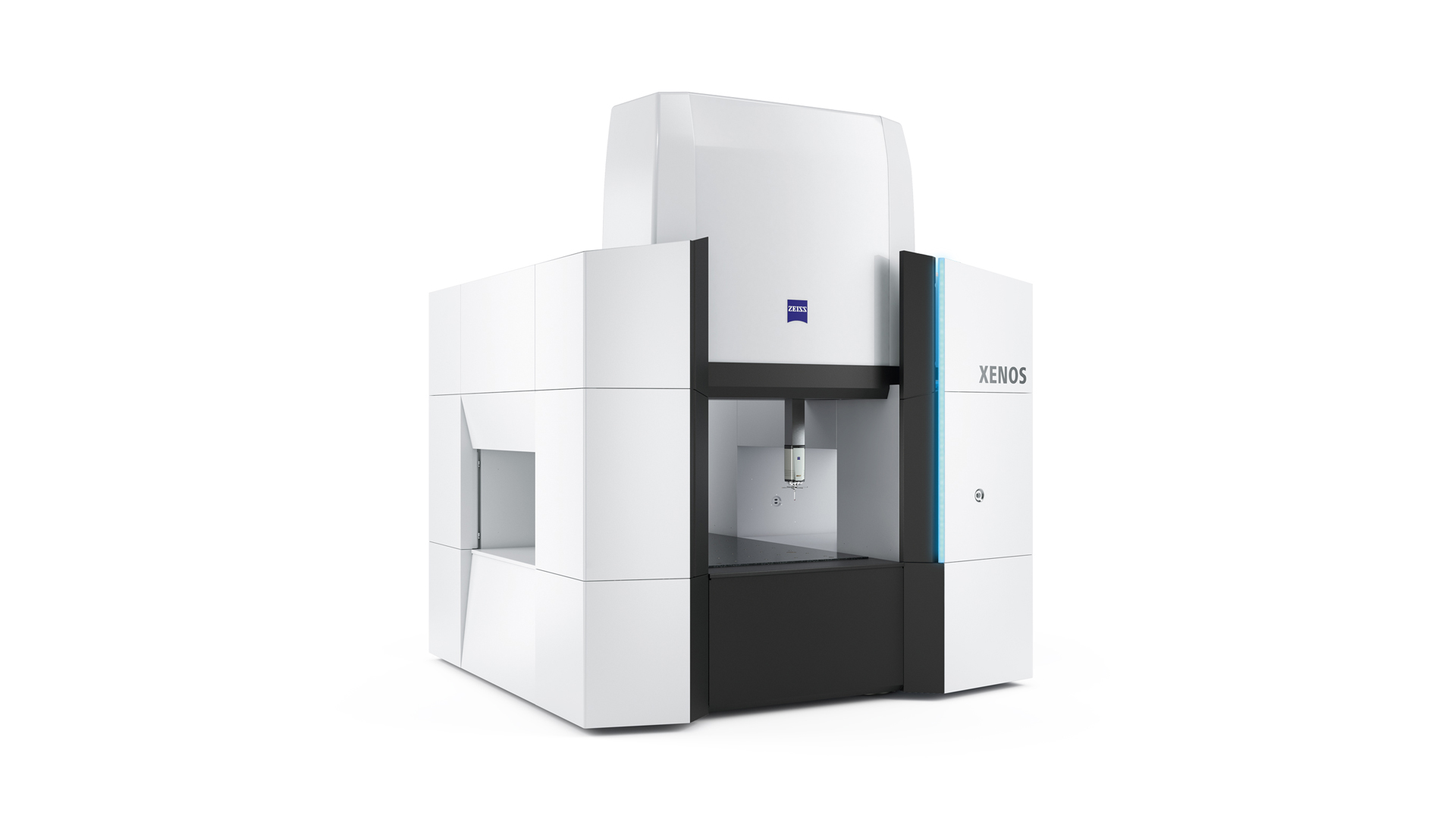

Source: Carl Zeiss Website(https://www.zeiss.com/metrology/products/systems/cmm.html)
Utilizing linear drive on all axes, this CMM boasts high precision with a maximum permissible length measurement error of 0.3+L/1000μm, repeatability of ±0.2μm, and resolution of 0.001μm. The reduced occurrence of errors allows for a decrease in the need for remeasurement.
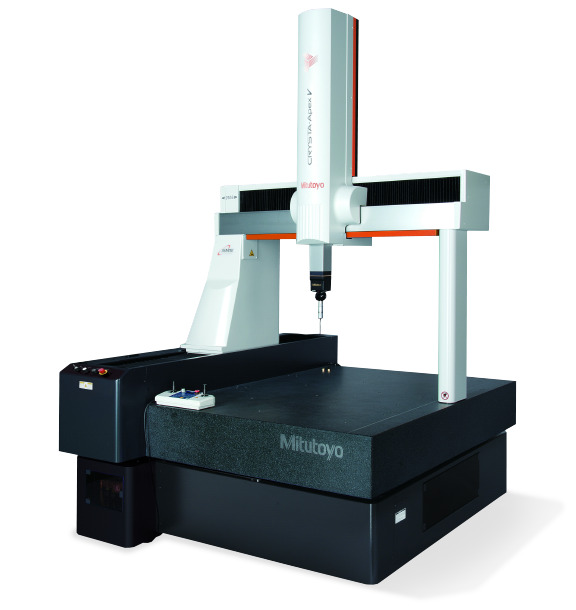

Source: Mitutoyo Website(https://www.mitutoyo.com/products/coordinate-measuring-machines/)
A CNC CMM that was first developed in 1976.
It features applications that respond to the demand for "Smart Factories" by allowing monitoring of operational status and maintenance management of the machine through the network.
Reasons for Selection